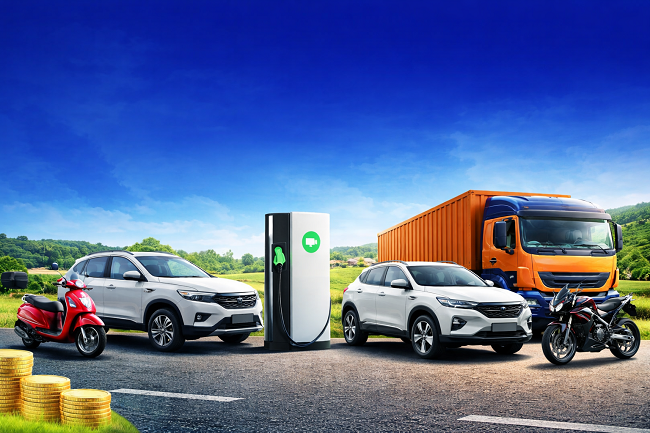
India’s automobile industry witnessed a strong and resilient performance in Calendar Year (CY) 2025, emerging as one of the key pillars of the country’s economic momentum. Total vehicle retail sales reached 2,81,61,228 units, registering a 7.71% year-on-year (YoY) growth over CY 2024. This growth was not driven by a single market but by the combined strength of urban stability and rural resurgence, making urban–rural market dynamics central to India’s automobile growth story.

A Turning Point in 2025: Policy, Affordability, and Sentiment
The momentum in auto retail gained pace from September 2025 onwards, following the implementation of GST 2.0 rate rationalisation. Tax reductions across mass-market categories—including small cars, two-wheelers (up to 350cc), three-wheelers, and select commercial vehicles—significantly improved affordability. This policy support, combined with easing inflation and improved liquidity, boosted consumer confidence and translated into strong festive-season demand across both urban and rural regions.
Segment-wise Performance: Urban Demand Meets Rural Scale
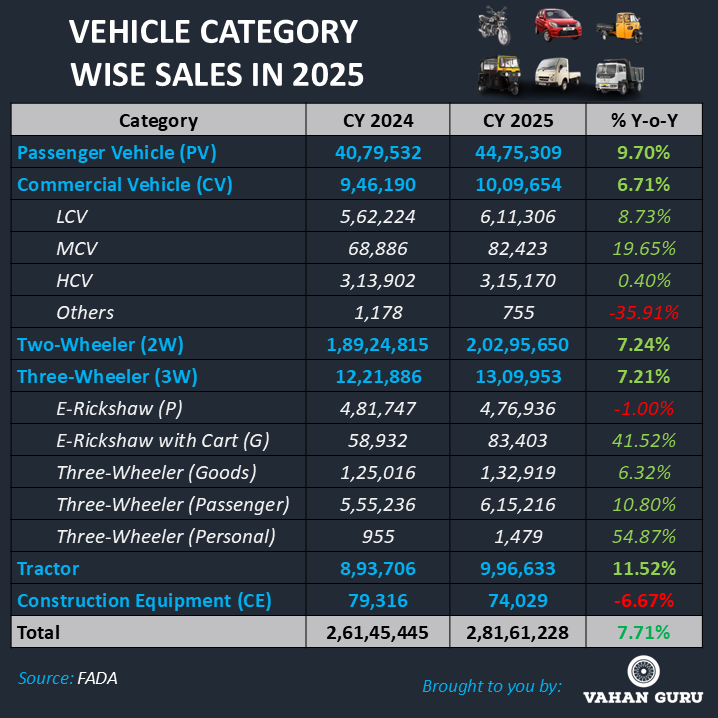
Passenger Vehicles (PV) delivered one of the strongest performances in CY 2025, with sales rising to 44,75,309 units, up from 40,79,532 units in CY 2024, marking a 9.70% YoY growth. Compact SUVs, deeper rural penetration, and improved affordability post-GST rationalisation supported growth, while urban markets continued to lead premium and feature-rich vehicle demand.
Commercial Vehicles (CV) posted sales of 10,09,654 units in CY 2025, compared to 9,46,190 units in CY 2024, achieving a 6.71% YoY growth. Light and medium CVs outperformed on the back of logistics, infrastructure, and e-commerce demand, whereas heavy CV growth remained relatively muted.
Two-Wheelers (2W) remained the largest contributor to India’s automobile industry in CY 2025. Total sales stood at 2,02,95,650 units in CY 2025, up from 1,89,24,815 units in CY 2024, registering a 7.24% YoY growth. Rural markets played a decisive role in volume expansion, supported by improved agricultural income and mobility needs, while urban markets ensured steady demand and faster adoption of electric two-wheelers.
Three-Wheelers (3W) recorded sales of 13,09,953 units in CY 2025, compared to 12,21,886 units in CY 2024, reflecting a 7.21% YoY growth. While passenger e-rickshaw volumes softened marginally, goods-oriented electric three-wheelers gained momentum, driven by last-mile delivery demand across urban and semi-urban regions.
Tractors emerged as a clear rural growth leader, with CY 2025 sales reaching 9,96,633 units, up from 8,93,706 units in CY 2024, registering a robust 11.52% YoY growth. Strong agricultural activity, stable farm incomes, and continued government support underpinned this performance.
Construction Equipment (CE) sales declined to 74,029 units in CY 2025 from 79,316 units in CY 2024, reflecting a 6.67% YoY contraction. The decline was primarily due to project execution delays, a high base effect, and an increasing preference for rental and shared equipment models.
Fuel Trends: EV and CNG Reshape Urban–Rural Choices
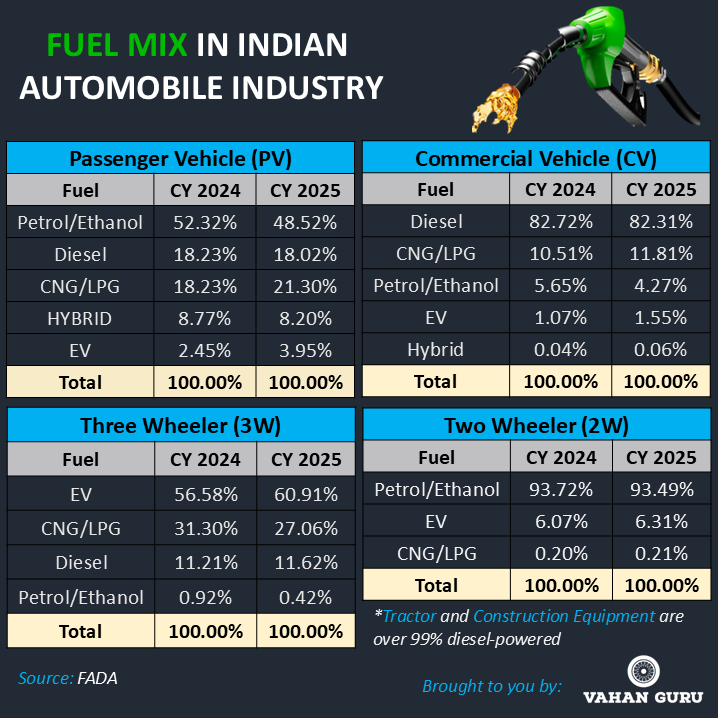
CY 2025 marked a decisive shift toward cleaner mobility across India. While petrol and diesel remained dominant, CNG and electric vehicles (EVs) gained rapid traction.
- Electric two-wheelers grew over 11%, driven largely by urban adoption.
- Electric three-wheelers surged more than 15%, supported by logistics and goods movement.
- In passenger vehicles, EV sales jumped 77% YoY, while CNG vehicles rose 28%, making CNG a preferred transition fuel in both urban and rural markets.
- Commercial vehicles saw rising adoption of CNG and EVs, though diesel continued to dominate heavy usage.
This fuel transition highlights a clear urban–rural convergence, where cities lead adoption while rural markets follow as infrastructure and cost economics improve.
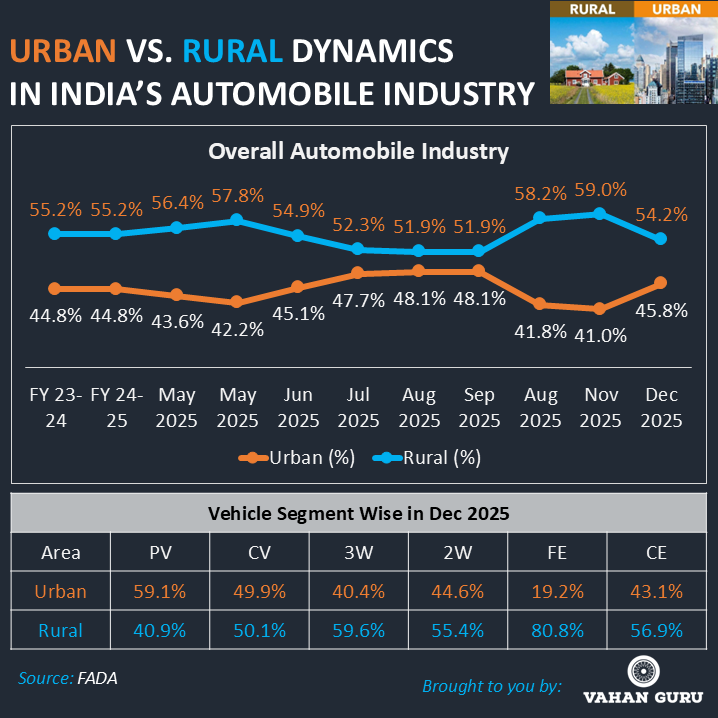
Rural India: The Engine of Volume Growth
Rural India has firmly established itself as the backbone of India’s automobile industry. Rural markets accounted for over 52% of total vehicle sales consistently across FY 2023–24, FY 2024–25, and CY 2025, peaking at 59% in November 2025. In contrast, urban markets maintained a steady 41–48% share, reflecting maturity and saturation in metros.
Key factors driving rural automobile demand include:
- Higher agricultural and allied incomes
- Improved credit availability and liquidity
- Strong seasonal and festive buying patterns
This structural shift underscores the importance of rural-focused product strategies, distribution expansion, and financing solutions for OEMs and dealers.
Outlook for 2026: Balanced, Sustainable Growth Ahead
Looking ahead to CY 2026, the Indian automobile industry is expected to witness steady and sustainable growth. Rural demand is likely to remain strong, supported by stable farm incomes and government spending. Urban markets will continue to drive innovation, premiumisation, and EV adoption.
Electric mobility is set to accelerate further with expanding charging infrastructure and broader model availability, while CNG will strengthen its role as a cost-effective transition fuel. Commercial vehicles should benefit from logistics, infrastructure, and capex-led growth, although heavy CV demand may remain moderate.
Conclusion
The Indian automobile industry’s growth story is no longer urban-centric or rural-dependent—it is powered by both. Urban markets bring innovation, early adoption, and value growth, while rural markets deliver scale, volume, and resilience. Together, they form the dual engines driving India’s automobile industry toward a more balanced, inclusive, and cleaner mobility future.





